Section outline
-
Powered by GraspOS project, this course addresses critical topics for advancing a responsible research assessment (RRA) system that fully embraces Open Science (OS) principles including:
- Open infrastructures for responsible research assessment
- Transparency and inclusivity of the assessment processes
- Recognition of contributions to Open Science
This training catalogue aims to provide to the stakeholders a guide to the use of indicators, tools, services and infrastructure to further assist their use in the context of implementing OS aware RRA approaches.
For each session, you can access the webinar videos, the links to the website, the presentation materials, links to articles and more.

-
-
GraspOS sets out the ambitious goal to develop, assess and put into operation an open and trusted federated infrastructure for next generation research metrics and indicators by offering data, tools, services and guidance to support and enable policy reforms for research assessment at researcher (individual/group), institutional, organisational and country level.
The SCOPE+i Framework (earlier OSAF - Open Science Assessment Framework) is designed to support the transition to Responsible Research Assessment (RRA), with a particular emphasis on contributions to OS. By integrating process resources and digital services into the SCOPE Framework by The International Network of Research Management Societies (INORMS), the SCOPE+i Framework combines the flexibility required to plan and conduct RRA in diverse assessment contexts with practical tools for managing the complexities of research assessment reform.
The assessment infrastructure - SCOPE+i Framework - has two main components:
- assessment process resources which offer guidance for implementing key elements of Responsible Research Assessment (RRA) such as SCOPE+i Resources and
- digital services which enable collaborative collection and sharing of assessment plans and documentation throughout the entire assessment process.
SCOPE+i Services consists of two digital services:
- Assessment Protocol Portfolio (APP) which brings together essential information for assessment planning – such as a readiness self-assessment, values statement, and purpose & context statement – along with the assessment protocol that outlines the assessment approach
- Openness Profile – a portfolio for making visible one’s contributions to Open Science (OS).
These services are part of the GraspOS Open Infrastructure and are technologically underpinned by the Research Activity Identifier, also known as RAiD.
As part of the broader GraspOS infrastructure, the SCOPE+i services offer three key advantages:
- Collaborative and Inclusive – Open to all assessment participants.
- Comprehensive Support – Accommodates all aspects of assessment planning, documentation, and final protocol development.
- Interoperable and Extensible – Built on a robust metadata schema and API, enabling direct data transfer to downstream analytic services. Additionally, individual instances of these Assessment Protocol Portfolios and Openness Profiles can be hierarchically linked to each other.
Assessment Protocol Portfolio
The SCOPE+i Assessment Protocol Portfolio (APP) supports the planning and documentation of research assessment by serving two key functions: it records the agreed-upon approach for a specific assessment event and provides a means to register the assessment protocol after the event concludes. It acts as a shared resource for conducting the assessment and documenting its outcomes.
An APP is a collaborative, multi-actor digital object that brings together essential information for assessment planning—such as a readiness self-assessment, values statement, and purpose statement—along with the assessment protocol that outlines the assessment approach.
During the assessment, the portfolio is accessible ("locally open") to all participants involved in the event. It can also be made publicly available afterward, balancing transparency with the need for privacy during the process. This approach ensures consistency and clarity for both evaluators and those being assessed, while protecting sensitive information during the event.
After the assessment concludes, the APP can be archived for historical reference. Additionally, the assessment protocol itself—separate from any privacy-related content—can be published in the Assessment Protocols Registry. This allows the broader community to learn from the protocol's design in relation to its local context and stated purpose.
The Assessment Protocols Registry serves as a shared knowledge base to inform and inspire the design of future assessment events.
Openness Profile
The primary goal of the Openness Profile is to make Open Science (OS) activities visible as a distinct and independent information entity, thereby promoting a more diverse and comprehensive consideration of OS in research and related assessment processes.
The Openness Profile supports the diversity of Open Science contributions by allowing flexible input of various types of content, including both quantitative and qualitative information. Qualitative information is captured through narratives, which enable structured, evidence-based input to support research assessment.
A dedicated narrative CV template is being developed within the GraspOS project and will be available for use during the piloting phase of the Openness Profile. These narratives can be supported by the Openness Profile, where relevant evidence-based input is included. Quantitative information refers to data that can be measured or counted using numerical values.
The Openness Profile can also be used in assessment contexts, either directly or as a general-purpose portfolio. In direct use cases, OS contributions recorded in an Openness Profile can be integrated into local assessment infrastructures. Alternatively, the Openness Profile can function as a portfolio of all relevant contributions—OS-related or otherwise—for a specific assessment event.
In both cases, Assessment Protocol Portfolios and Openness Profiles can be hierarchically linked. For instance, linked information may share a common landing page and be accessible through an API.
Read more:
Please note: The SCOPE+i Framework was earlier called "Open Science Assessment Framework (OSAF)".
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
In the GraspOS project, the Open Science Assessment Framework (OSAF) is focused on enabling Responsible Assessment (RRA), as it forms the basis of assessing Open Science. The OSAF has three elements: the SCOPE+i method (SCOPE plus infrastructure), digital Assessment Portfolios, and an Assessment Registry. In this webinar we will introduce the OSAF and provide a concrete use case of the Assessment Portfolio (also known as the Openness Profile).
In this webinar you will hear about the GraspOS project’s work on the OSAF. The OSAF will enable a system based on rewards and recognition using a new generation of qualitative and quantitative metrics and indicators. You will hear about the RRA and how it relates to Open Science and about the various frameworks that guide our work, e.g. OS-CAM, Nor-CAM, Opus RAF and SCOPE. The main goal of OSAF is to translate principles into practice with the help of CoARA and SCOPE frameworks, which will provide practical guidelines in terms of points to consider when planning on implementing OS research assessment into an organisation’s workflow. Lastly, you will learn how to apply the SCOPE-i method, Assessment Portfolio and Assessment Registry in different assessment event phases. One part of the Assessment Portfolio consists of an Openness Profile, which documents relevant contributions to Open Science that are essential to research but still unrecognised by the current research evaluation practice. To showcase the Openness Profile in concrete terms, we will introduce the work from the viewpoint of a pilot - the Finnish research.fi service.
Presentation on the Open Science Assessment Framework (OSAF), covering its agenda, key concepts and the Openness Profile use case. Tatum, C., Nordling, J., & Anli, Z. (2024, March 7th). GraspOS Webinar The Open Science Assessment Framework. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10794055. All version can be cited by using DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10794054
Recording of the Open Science Assessment Framework (OSAF) webinar held on 7 March 2024.
Objectives & preferred outcomes:
-
Disseminate concept
-
Concrete use case
-
Feedback on usability
Please note: The term "OSAF" was later changed to "SCOPE+i Framework" .
-
-
Explore
- the ppt-presentation Introduction to SCOPE+i Resources.pdf
- Description of the SCOPE+i Resources
Get to know
- Why familiarize yourself with SCOPE+i Resources
- What are SCOPE+i Resources
- What is the contents of each SCOPE+i Resources
- Basic idea of the SCOPE Framework
- How SCOPE+i Resources are aligned with the phases of SCOPE Framework
- Where can you find SCOPE+i Resources
- Re-use permissions of SCOPE+i Resources
Learning objectives
After completing the course section the learner
- utilizes SCOPE+i Resources e.g. templates to fit their organization´s needs
- utilizes, applies and adapts SCOPE+i Resources in RRA processes and in training and/or orientation sessions they is involved in
- is aware of the variety of OS contributions and activities
- understands the practical purpose of the five phases of SCOPE Framework
Supplementary material
- GraspOS Course: EOSC Finnish Forum Webinar: GraspOS benefits to Finnish organisations | OpenPlato (slides and recorded webinar)
- GraspOS Course: SCOPE+i Framework as key result of GraspOS | OpenPlato
-
Ppt-presentation on introduction to SCOPE+i Resources
-
Short summary of the contents of SCOPE+i Resources supplemented with links to full texts in Zenodo
-
EOSC Finnish Forum webinar 24th March 2025 looked at how the solutions developed in the GraspOS project advance open-science-aware responsible research assessment. Learn how pilot work related to the Research.fi service, as well as resources to support assessments and a new hybrid-indicator can benefit Finnish organisations, especially from the point of view of open science practices.
In this webinar the Finnish partners of GraspOS, CSC - IT Center for Science, University of Eastern Finland and the Federation of Finnish Learned Societies are joining forces and presenting their work done in these contexts.
Agenda:
- Introduction to GraspOS / Laura Himanen, CSC - IT Center for Science (5 min)
- Pilot work related to Research.fi (OpenCitations and Openness Profile) / Joonas Nikkanen, CSC - IT Center for Science (15 min)
- Developing resources to support responsible research assessments as part of the Open Science Assessment Framework (OSAF) / Elina Koivisto, Tiina Sipola, Federation of Finnish Learned Societies (15 min)
- Hybrid Indicator for the Evaluation of Societal Interactions of Open Science / Katri Rintamäki, Heikki Laitinen, Anni Tarkiainen, University of Eastern Finland (15 min)
- Q&A (15 min)
GraspOS benefits to Finnish Organisations-National event - GraspOS
presentations (PDF) and webinar
-
-
-
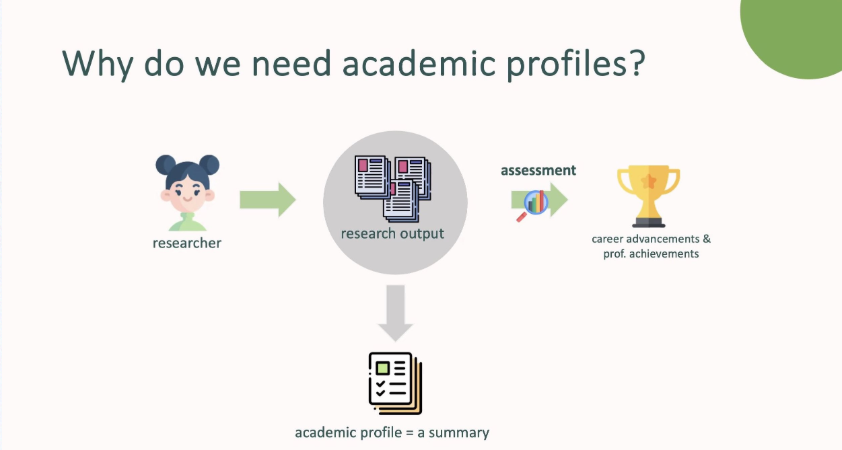
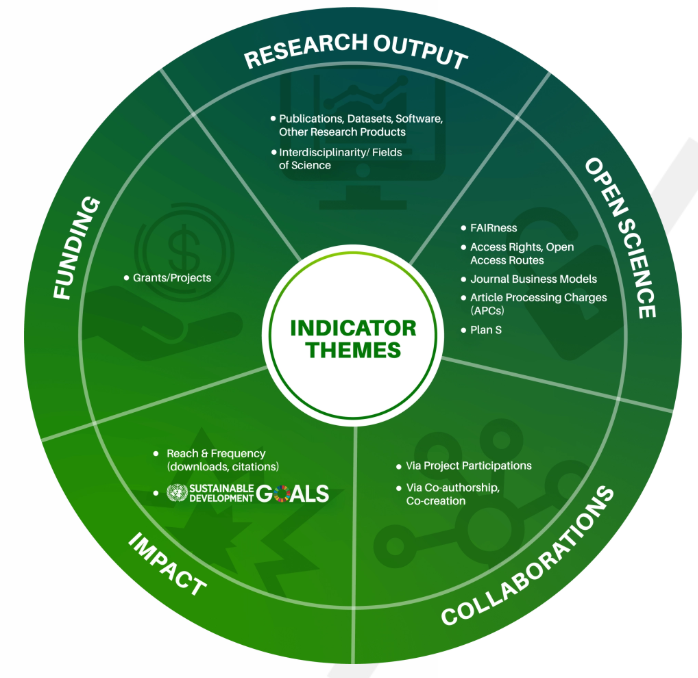
Presentation slides from the BIP! Scholar training event, explaining how researchers can create academic profiles to highlight their work, contributions, and career narratives with customizable views.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10067214 -
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the BIP! Scholar webinar that took place on November 2nd, 2023, showcasing how researchers can create detailed academic profiles to highlight their work, roles, and career narratives.
-
-
Slides from GraspOS's 4th training session on using OPERAS Metrics to measure and showcase the impact of Open Access books.
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the GraspOS training session 'Leveraging OPERAS Metrics' (26 Nov 2024), demonstrating how to measure and showcase the impact of Open Access books.
-
-
Presentation from GraspOS's 3rd webinar on PEP-CV, exploring peer-mentored Narrative CVs as a tool for academic recognition and research culture reform.
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the PEP-CV webinar (11 Feb 2025) on peer-mentored Narrative CVs, a transformative approach to academic assessment aligned with DORA and CoARA, promoting inclusivity and broader research contribution recognition.
-
Indicators for Institutions - OpenAIRE MONITOR: Acknowledge, understand and place thyselves in the research landscape unlocking Research Excellence.
-
Training slides on navigating the research landscape with OpenAIRE Monitor, emphasizing institutional tracking of outputs to unlock research excellence.
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the OpenAIRE Monitor webinar (19 Dec 2023) on using institutional indicators to map research excellence and navigate the scholarly landscape.
-
Article summarizing the OpenAIRE Monitor training webinar, focusing on institutional indicators and their role in assessing research impact.
-
-
Slides from the GraspOS webinar on assessing Open Access books, featuring PRISM (Peer Review Information Service for Monographs) and its role in transparent research evaluation.
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the GraspOS webinar (14 May 2024) on assessing Open Access books using PRISM (Peer Review Information Service for Monographs) to enhance transparency in peer review tracking.
-
-
Learn how FAIR is your metadata and the compliance with OpenAIRE Guideline s.Discover how the OpenAIRE Metadata Validator can help you improve the quality, openness, FAIRness and interoperability of your metadata. Whether you manage a repository, CRIS, aggregator or journal platform, this session will show how the Validator supports both compliance with OpenAIRE Guidelines and alignment with FAIR principles — helping you make your content more visible and reusable across the Open Science landscape.
-
Learn how FAIR is your metadata and the compliance with OpenAIRE Guideline s.Discover how the OpenAIRE Metadata Validator can help you improve the quality, openness, FAIRness and interoperability of your metadata. Whether you manage a repository, CRIS, aggregator or journal platform, this session will show how the Validator supports both compliance with OpenAIRE Guidelines and alignment with FAIR principles — helping you make your content more visible and reusable across the Open Science landscape.
-
Learn how FAIR is your metadata and the compliance with OpenAIRE Guideline s.Discover how the OpenAIRE Metadata Validator can help you improve the quality, openness, FAIRness and interoperability of your metadata. Whether you manage a repository, CRIS, aggregator or journal platform, this session will show how the Validator supports both compliance with OpenAIRE Guidelines and alignment with FAIR principles — helping you make your content more visible and reusable across the Open Science landscape.
-
-
Slides of the 3rd Training event of GraspOS entitled "Citation and their meaning - or why we cite".
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-
Recording of the GraspOS training (23 July 2024) on citation analysis, exploring the meaning and intent behind scholarly citations, and introducing tools to classify citation functions in research.
-
-
This is the presentation of an exclusive webinar held on Tuesday, 29 April 2025, to explore the enhanced OpenAIRE Graph API! Designed to support bibliometric analyses, research discovery, and Open Science monitoring, the new API offers streamlined access to OpenAIRE’s rich research data ecosystem. Learn about its key features, real-world applications, and how it can help institutions, librarians, researchers, and developers gain deeper insights.
-
This is an exclusive webinar to explore the enhanced OpenAIRE Graph API! Designed to support bibliometric analyses, research discovery, and Open Science monitoring, the new API offers streamlined access to OpenAIRE’s rich research data ecosystem. Learn about its key features, real-world applications, and how it can help institutions, librarians, researchers, and developers gain deeper insights. Plus, get your questions answered in our live Q&A session!
-
GraspOS training website featuring events, resources, and guidance on Open Science-aware assessment tools, indicators, and services for stakeholders.
-